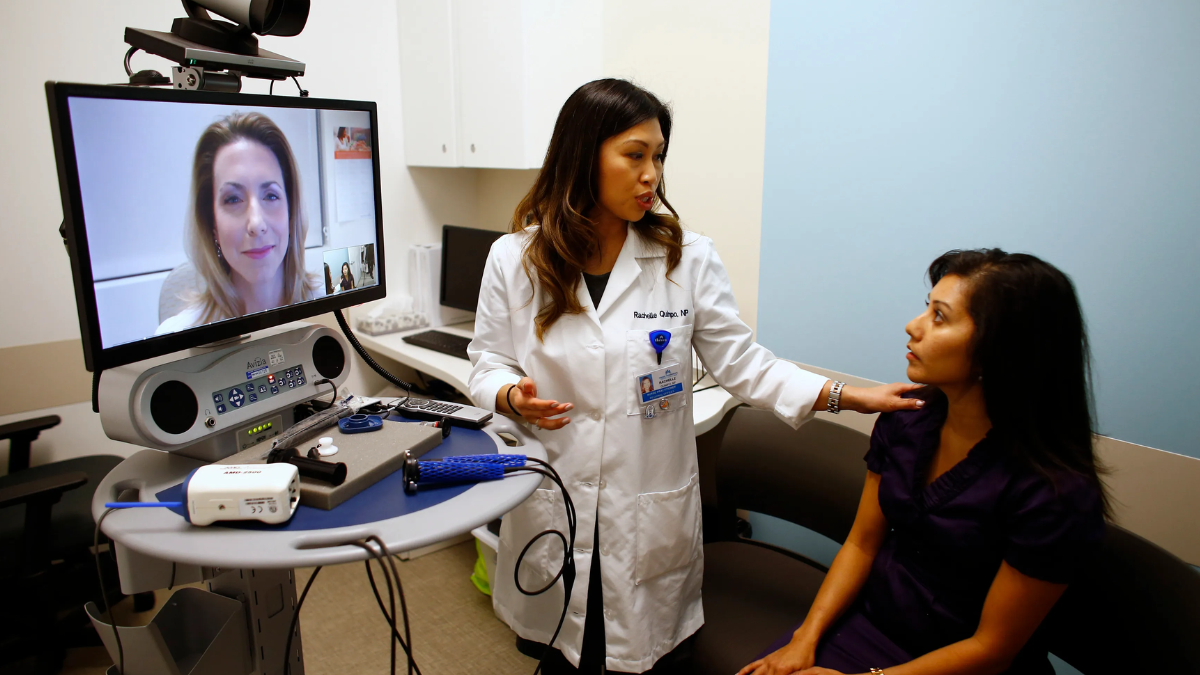
Telemedicine is transforming healthcare delivery by enabling hospitals to provide medical consultations, diagnoses, and follow-up care remotely. The adoption of telemedicine has accelerated due to technological advancements, increased patient demand for convenience, and the need to maintain healthcare access during emergencies such as pandemics. Hospitals are integrating telemedicine into their services to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and expand access to care.
Expansion of Remote Consultations
Hospitals now offer remote consultations across multiple specialties including general medicine, dermatology, psychiatry, cardiology, and endocrinology. Patients can schedule virtual appointments through secure platforms, discuss symptoms with physicians, and receive medical advice without visiting the hospital physically. Remote consultations reduce travel time, minimize exposure to contagious illnesses, and improve healthcare accessibility, particularly for patients in rural or underserved areas.
Integration with Electronic Health Records
Telemedicine platforms are increasingly integrated with electronic health records (EHRs), allowing physicians to access patient histories, lab results, and imaging reports during virtual consultations. This integration ensures continuity of care, accurate diagnosis, and informed treatment plans. Patients benefit from seamless communication between virtual and in-person visits, maintaining a complete and up-to-date medical record.
Remote Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management
Hospitals use telemedicine to monitor patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and respiratory disorders. Wearable devices and mobile applications transmit real-time data on vital signs, glucose levels, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation to healthcare providers. Physicians can track progress, adjust medications, and provide timely interventions, reducing hospital readmissions and enhancing disease management.
Tele-ICU and Critical Care Support
Telemedicine extends to intensive care units (ICUs) through Tele-ICU programs, enabling specialists to monitor critically ill patients remotely. Using high-definition cameras, sensors, and real-time data feeds, physicians can collaborate with on-site staff to manage complex cases, adjust treatment protocols, and respond to emergencies promptly. Tele-ICU systems improve patient safety, reduce mortality rates, and optimize ICU resource utilization.
Mental Health and Counseling Services
Hospitals are increasingly providing mental health consultations via telemedicine. Patients can access psychiatrists, psychologists, and counselors through secure video calls, ensuring timely support for stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health concerns. Tele-mental health services overcome barriers such as stigma, transportation, and geographic limitations, enabling broader access to psychological care.
Tele-Surgery and Remote Specialist Support
Some hospitals are adopting tele-surgery systems, allowing surgeons to guide procedures remotely or provide real-time support to on-site surgical teams. High-definition cameras, robotic systems, and live communication enable specialists to assist in complex surgeries, share expertise across locations, and enhance surgical outcomes. Remote specialist consultations also allow patients to access expert opinions without traveling long distances.
Benefits for Patients and Hospitals
Telemedicine improves patient convenience, reduces travel costs, and increases access to healthcare professionals. For hospitals, telemedicine enhances operational efficiency, optimizes resource allocation, reduces patient load in outpatient departments, and expands service reach. It also supports infection control by minimizing in-person interactions during contagious disease outbreaks.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its advantages, telemedicine adoption faces challenges including data security, technology accessibility, and regulatory compliance. Hospitals address these issues by implementing secure, encrypted platforms, providing patient training for technology use, and adhering to telehealth regulations and guidelines. Continuous feedback from patients and healthcare providers helps refine telemedicine services and ensures quality care.
Future of Telemedicine in Hospitals
The future of telemedicine includes AI-powered diagnostics, predictive analytics, virtual reality-based rehabilitation, and integration with wearable technology for continuous patient monitoring. Hospitals are likely to adopt hybrid care models combining in-person and virtual visits, expanding specialty services, and improving access for remote populations. Telemedicine is expected to become a standard component of hospital care, transforming how healthcare is delivered and experienced.
Conclusion
Hospitals are rapidly adopting telemedicine to improve patient care, enhance accessibility, and optimize healthcare delivery. Remote consultations, chronic disease monitoring, Tele-ICU support, mental health services, and tele-surgery are key areas of implementation. By integrating telemedicine with existing hospital infrastructure and electronic health records, healthcare providers can deliver safe, efficient, and patient-centered care. Telemedicine ensures that quality healthcare reaches patients wherever they are, making modern hospitals more flexible, responsive, and technologically advanced.
FAQs
Q1: What types of services can patients access via telemedicine?
Patients can access general consultations, specialist advice, mental health counseling, chronic disease monitoring, and follow-up care through telemedicine.
Q2: How do hospitals ensure patient privacy in telemedicine?
Hospitals use secure, encrypted platforms, comply with telehealth regulations, and integrate privacy protocols to protect patient information.
Q3: Can telemedicine replace in-person hospital visits?
Telemedicine complements in-person care. While routine consultations, follow-ups, and monitoring can be done remotely, procedures, surgeries, and emergencies still require physical visits.
Q4: Is telemedicine effective for chronic disease management?
Yes, remote monitoring and virtual consultations allow continuous management of chronic diseases, timely medication adjustments, and reduced hospital readmissions.
Q5: What technology is required for telemedicine?
Telemedicine requires secure video conferencing platforms, wearable monitoring devices, internet access, and integration with electronic health records for seamless care.